The company must satisfy each performance obligation by providing the goods or services to the customer. The company can recognize revenue when it’s completed the performance obligations, and control of the goods or services has been transferred to the customer. In other words, the revenue recognition principle is a crucial concept in accounting that guides the recognition and reporting of revenue in a company’s financial statements.
Point of sale method to recognize revenue
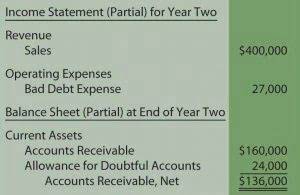
Then, in Year 2, the inventory will show a decrease while the accounts receivable shows an increase from the sale. Finally, in Year 3, when the customer settles their bill, accounts receivable will show a decrease, while cash will see an increase. Since this party cannot be matched to any individual sale, it can be recognized under the immediate allocation method as an expense in the period it was paid.
- Assume the landscaping workload is distributed evenly throughout the six months.
- Here, we do take into consideration variables such as discounts, refunds and rebates, if any.
- For example, assume that a company paid $6,000 in annual real estate taxes.
- When this matching is not possible, then the expenses will be treated as period costs.
- The revenue recognition principle dictates the process and timing by which revenue is recorded and recognized as an item in a company’s financial statements.
- One of the most common mistakes made by people unfamiliar with the accrual basis of accounting is conflating revenue earned and recognized with cash payments collected.
- The matching concept or revenue recognition concept is not used in the cash accounting method.
Conditions for Revenue Recognition
- From the following transactions, prepare journal entries for Jamal’s Music Supply.
- Although you have a payment on the books, you shouldn’t recognize any revenue for the job yet because your obligations have not been fulfilled.
- Revenue is recognized when the building is completed and transferred to the customer.
- This step involves all parties involved agreeing to the terms of the contract, where contracts can be in written or non-written format, such as verbal commitments.
- In other words, the standardized ASC 606 revenue recognition steps produce reports that make it easier for investors, analysts, and regulators to see what’s really going on at a company.
- These methods can significantly impact financial reporting and when income is recognized on a company’s financial statements.
And, thankfully, they do—because these guidelines give busy accounting teams the tools they need to correctly recognize revenue so their companies’ financial reports remain accurate and consistent. Deferred revenue represents unearned revenue that a company has received but not yet recorded on its income statement. Income revenue commonly referred as revenue recognition, states that revenue should be recognized only when it is earned irrespective of whether cash transaction has occurred.

What are some of the biggest compliance challenges of implementing ASC 606?

At the beginning as the organization has not received any payment they will have accounts receivables of $10,000. As the installment is received each month, the accounts receivables will be debited with the installment amount of $2000 and the revenue will be recognized. The revenue recognition principle under ASC 606 states that https://www.bookstime.com/ revenue can only be recognized when the promised goods or services are delivered to the customer. A core part of accrual accounting, the revenue recognition principle is integral to the GAAP principle. Apart from GAAP, the revenue recognition principle is also integral to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Regulators know how tempting it is for companies to push the limits on what qualifies as revenue, especially when not all revenue is collected when the work is complete.
- Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
- Not to mention how error-prone it is, given all the spreadsheets involved.
- Under the cash basis of accounting, you should record revenue when a cash payment has been received.
- For example, a company that sells products on an installment plan would use the installment method to recognize revenue.
- Goods and services that are not distinct can be combined with other goods and services until they are distinct, post which we can recognize them as a performance obligation in the contract.
Identification of the contract with the customer
Some of the more challenging and judgmental aspects of applying the revenue standard are highlighted below. High-level summaries of emerging issues and trends related to the accounting and financial reporting topics addressed in our Roadmap series, bringing the latest developments into focus. IAS 18 states that ‘Revenue shall be measured at the fair value of the consideration received or receivable’ (12).

A Small Business Guide to the Revenue Recognition Principle
Revenue recognition at the time of sale is a primary component of accrual accounting. Under accrual accounting, any event that generates a sale constitutes the requirement for recognition of revenue on that date. Revenue recognition events can take a multitude of forms as businesses provide a variety of services and goods to their customers. Revenue recognition events according to the revenue recognition principle can include purchase orders or billable hours. Since this is such an important account for your growing business and the client has been established for decades, you extend them net-60 payment terms. As soon as the installation of the program is complete, you have satisfied all of the criteria for revenue recognition under the accrual basis of accounting.
Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations
Using BWW as the example, let’s say one of its customers purchased a canoe for $300, using his or her Visa credit card. To recognize revenue under IFRS, conditions under three categories i) performance ii) collectability iii) measurability must be fulfilled. In other words, the revenue is recognized in the same accounting period in which the expense is recorded. The revenue recognition principle is a crucial accounting concept that guides how revenue should be recognized and recorded in a company’s financial statements. By understanding the revenue recognition principle and its criteria, methods, and challenges, companies can ensure they get accurate financial information, ultimately impacting their profitability and financial health. The backgroundAs already stated, revenue is a crucial number to users of financial statements in assessing an entity’s financial performance and position.
- If it’s not probable that the company will collect the consideration, revenue can’t be recognized.
- In the United States, Deloitte refers to one or more of the US member firms of DTTL, their related entities that operate using the “Deloitte” name in the United States and their respective affiliates.
- This highlights how revenue from contracts with customers is treated, providing a uniform framework for recognizing revenue from this source.
- It is expected that these items will last five years and have no residual value for resale.
- When ASC 606 was issued in 2014, it significantly transformed revenue recognition practices in the US by introducing a unified and principles-based framework that aligns GAAP with international accounting standards.
- For most CFOs and accountants, Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are like the holy grail of accounting—mastered and internalized over years of heavy usage and application.
Get out of spreadsheets and workarounds. Get back to accounting.

Focusing on today, the revenue recognition principle is a concept you need to know about at all costs. It is the mere foundation that shows investors, stakeholders, and the market at large all about how a company is doing financially and operation-wise. As you can see from the question itself, this term is highly vital and means a lot to numerous people. This is where you record the revenue once the product or service has reached the respective customer, despite whether the form of payment was credit or cash. When we say the revenue has been “realized”, it simply means that the customer has successfully received the service or product but won’t pay until later.
In this case, the revenue is recognized once the entire contract, along with the performance obligations, are fully satisfied. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), on the 28th of May, 2014, introduced the ASC 606 revenue recognition. In layman’s terms, this new standard depicts how a company should manage its revenue from customer contracts, clearly showing a consistent and transparent method for recognizing revenue alike. Also under the accrual basis of accounting, if an entity receives payment in advance from a customer, then the entity records this payment as a liability, not as revenue.